Par Dr. Serge Marchand
6 - Mécanismes endogènes
Journées de formation sur les bases neurophysiologiques
de la douleur et son traitement
Serge Marchand, Ph.D.
Endogenous Pain
modulation Mechanisms
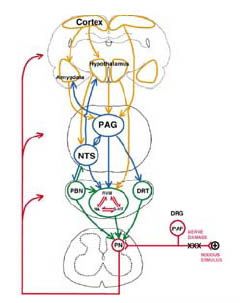
1
Inhibition vs facilitation
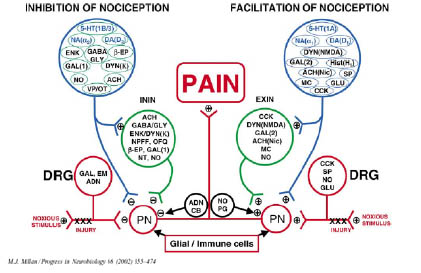
2
SEROTONINE

3
NORADRENALINE
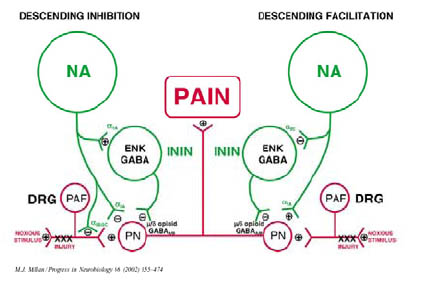
4
DOPAMINE
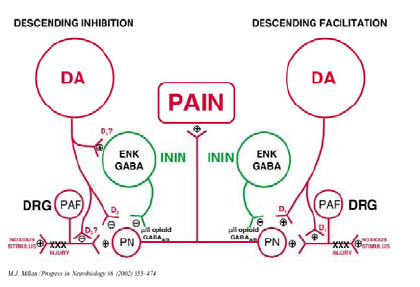
5
Endogenous Pain
Inhibitory Systems
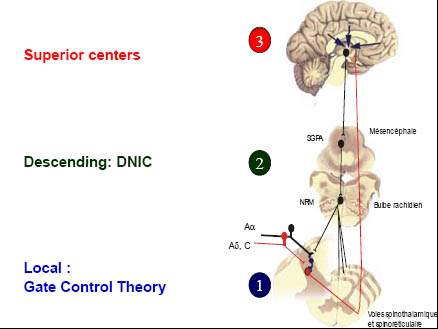
6
Endogenous Pain
Inhibitory Systems
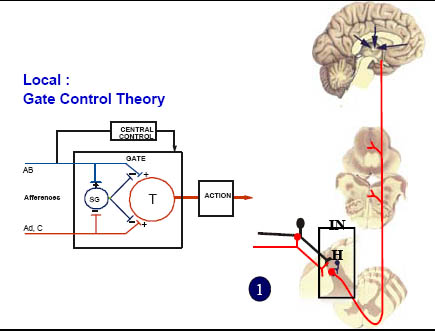
7
Deconstructing the Gate Control Theory
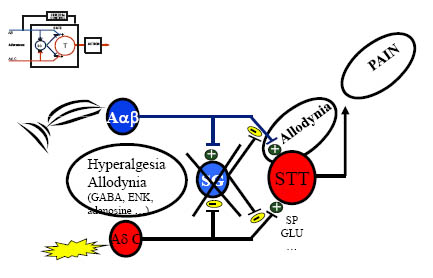
8
Clinical Application
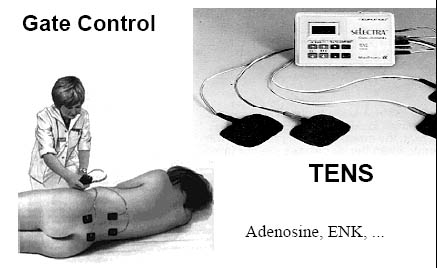
9
TENS et caféine
Effet de la caféine
► Récepteurs = adénosine
► antagoniste= caféine

10
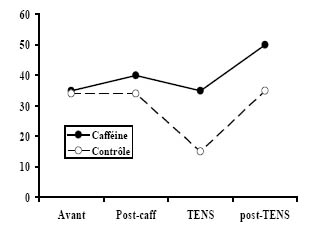
Marchand S, Li J, Charest J. Effects of caffeine on analgesia from transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation. N Eng J Med 333(5):325-326, 1995.
11
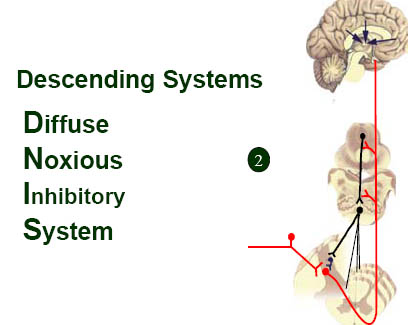
Endogenous Pain Inhibition
12

13

14
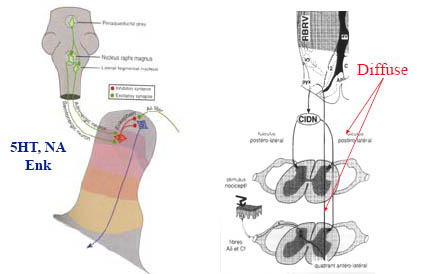
Descending inhibition
15
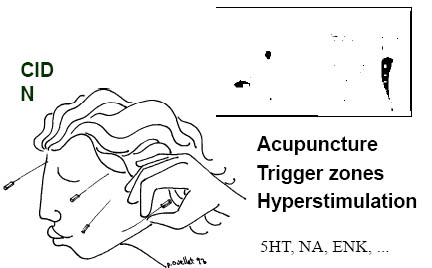
Clinical applications
16

17
SPATIAL SUMMATION and NOCICEPTION

18
Sommation spatiale et douleur
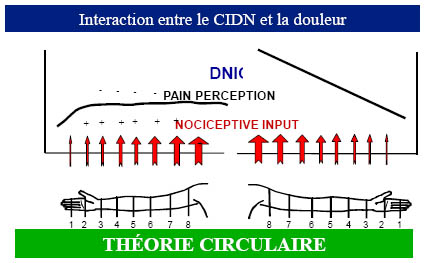
19
Cold Water Finger-
Shoulder Control subject
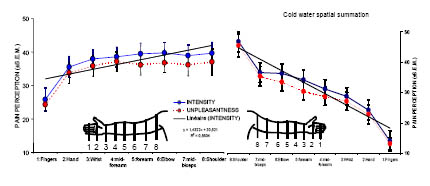
20
SPATIAL-DNIC

21
SPATIAL-DNIC
22
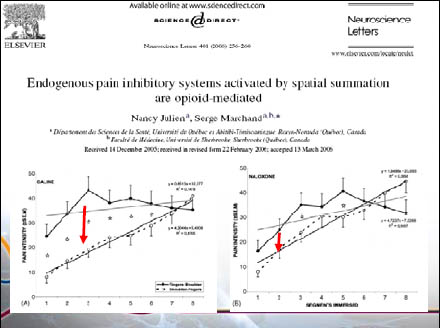
23
DNIC method
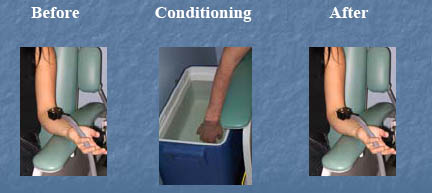
24

25

26
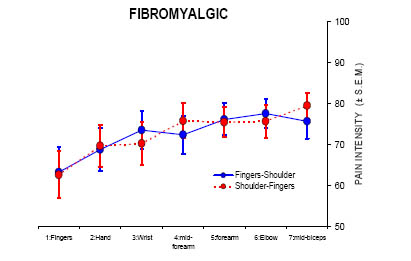
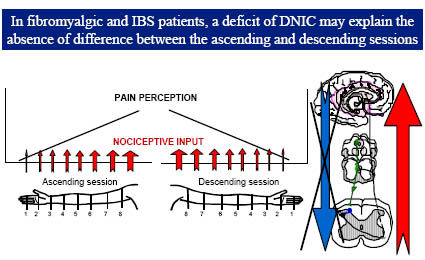
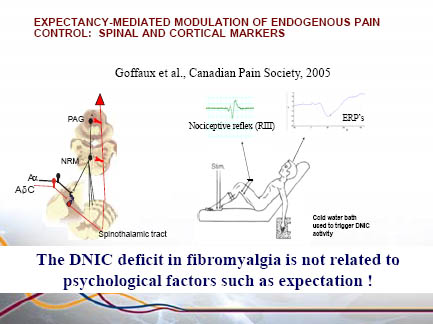
Endogenous Inhibitory System Dysfunction
Unique to diffuse pain, like in fibromyalgia, or present in all chronic pain conditions?
27

28
Spatial summation in fibromyalgia
Considering:
• Reduction of 5HT and NA in CSF of fibromyalgic patients
• Role of 5HT and NA in DNIC
• =Dysfunction of endogenous pain modulation (DNIC-like) in fibromyalgia?
29
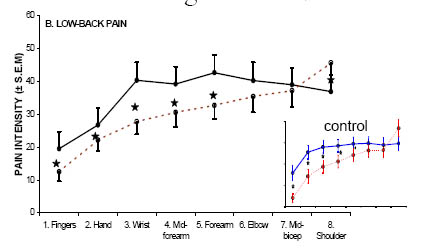
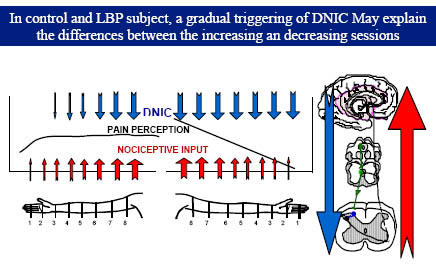
Lombalgia and DNIC
30
SPATIAL-DNIC
31
SPATIAL-DNIC
32
Endogenous pain
modulation mechanisms
33

34
Applications Cliniques
Centre supérieurs

Hypnose
Biofeedback
Approches cognitives
35
TEP et HYPNOSE
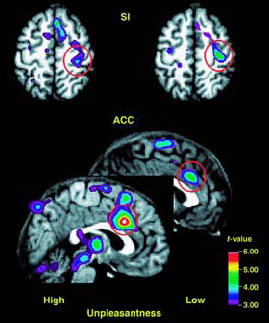
P. Rainville et al., Science 277:968-971, 1997.
36
PLACEBO

37
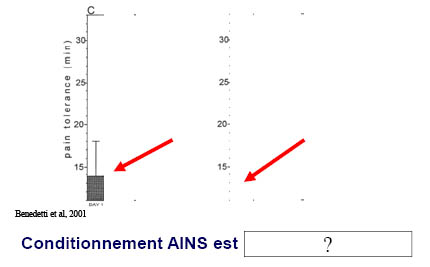
38

39
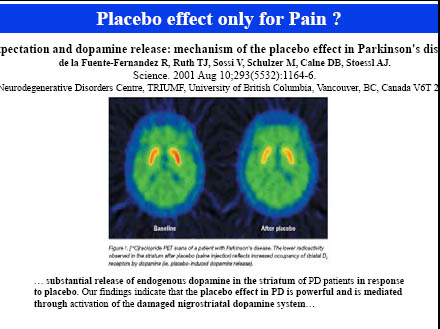
40
41
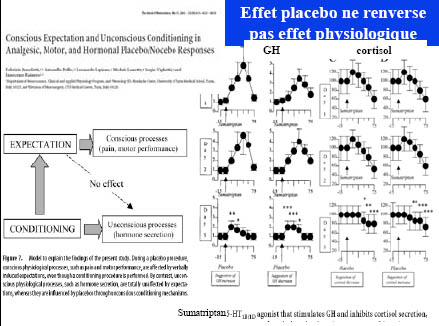
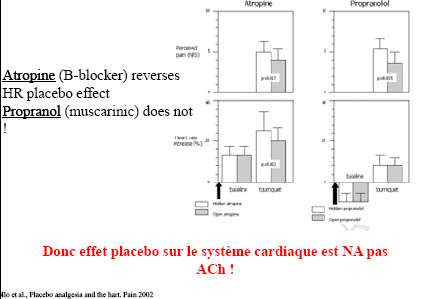
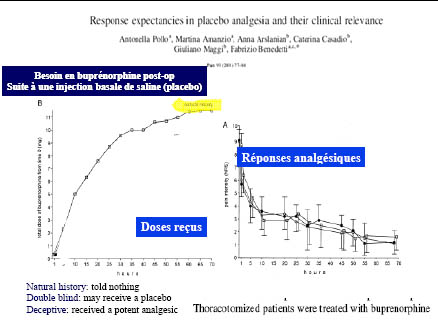
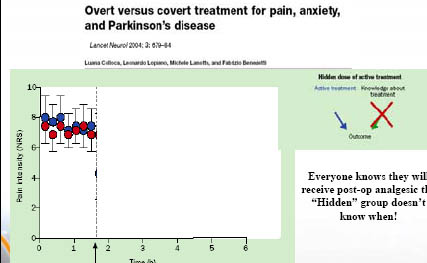
Différents systèmes = différents mécanismes ?
42
43
44
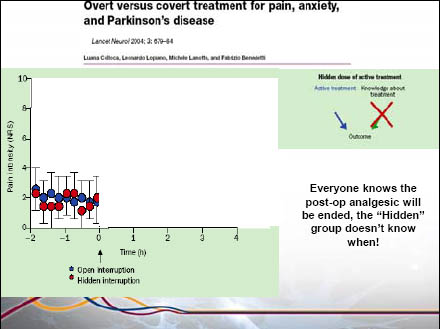
45
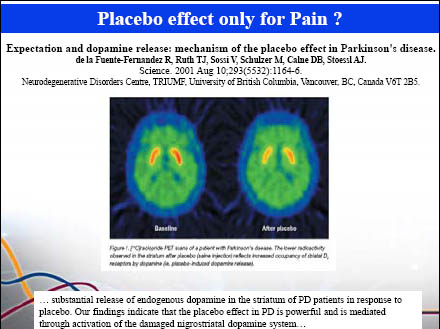
46
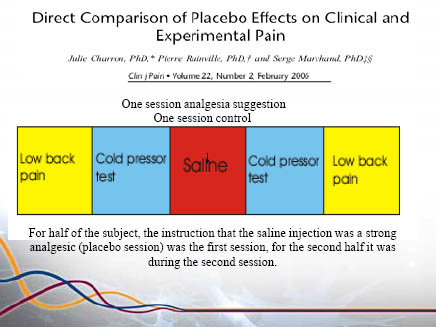
47
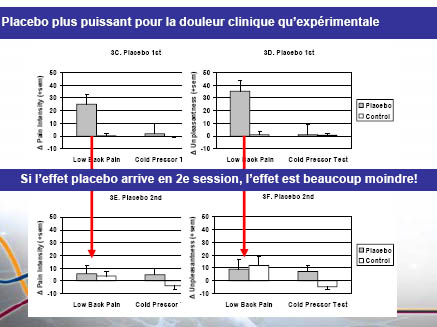
48
Rôle des centres supérieurs
• Réponse placebo supérieure pour les douleurs cliniques (rôle du désir de soulagement)
• Pré-exposition à un traitement connu pour être inefficace (saline) bloque l’effet analgésique des attentes (placebo)subséquentes
• Échelle OMS : amène à une préexposition à des traitements moins efficaces !

49

50
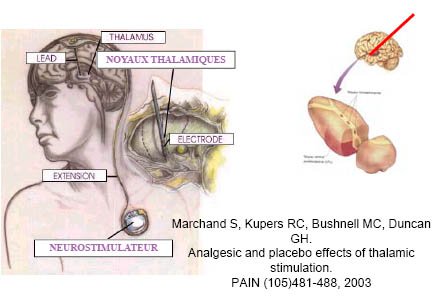
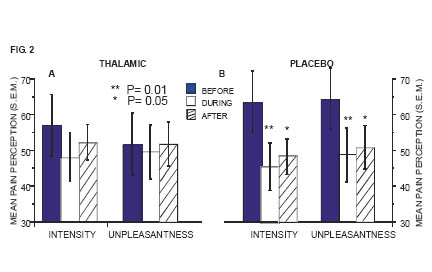
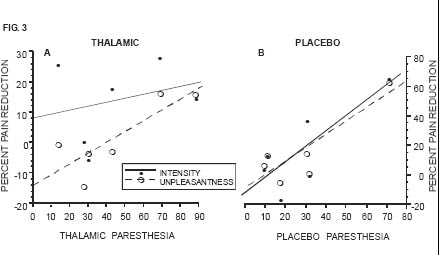
Stimulation thalamique
51
52
53
54
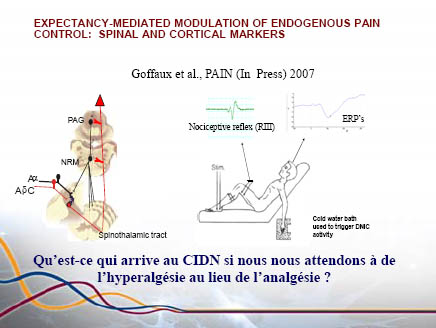
Expectation mediated Cerebrospinal modulation of the analgesia
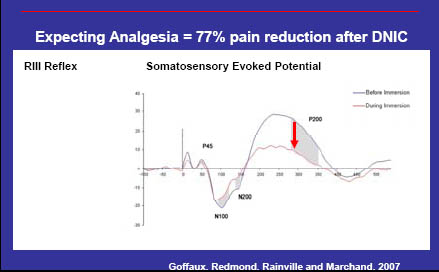
55
Expectation mediated Cerebrospinal modulation of the analgesia
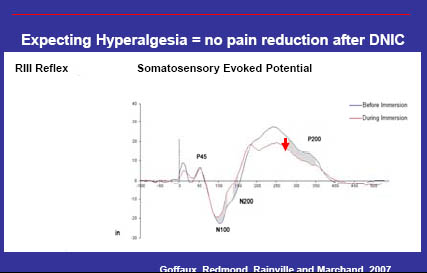
56
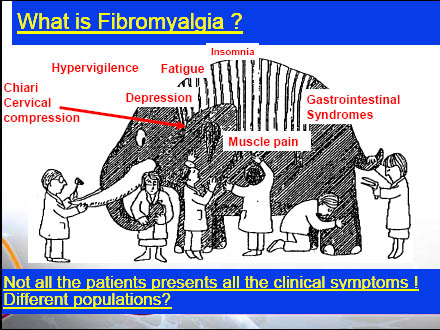
57
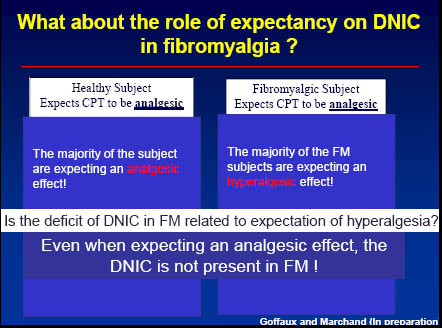
58
59
60
Expectation and pain
► Low Back School
► TENS
► Placebo
► Vertebral Manipulation
61
Regression: Patient-Doctor
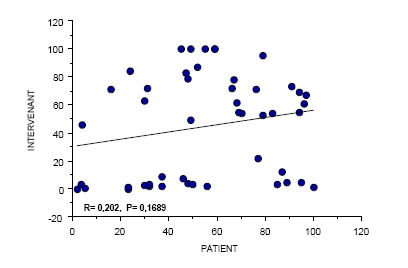
62
Regression: Doctor-Pain
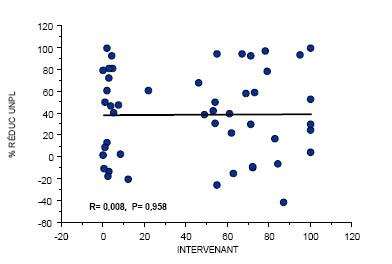
63
Regression: Patient-Pain
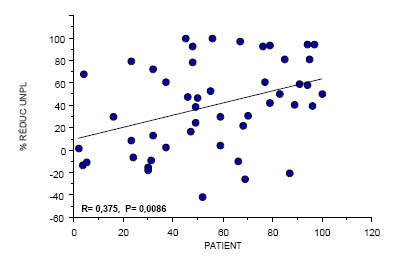
64
Conclusion
Patient’s expectations, not clinician’s expectations, are good predictors of pain relief
65
Complémentarité des approches pharmacologiques et non pharmacologiques
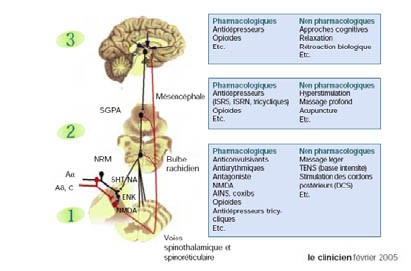
66

67
68
Serge Marchand, Ph.D.


